HepaFat-AI
Automated MRI Measurement Of Liver Fat
HepaFat-AI automatically analyses MRI datasets to assess liver fat in patients, providing doctors with a comprehensive, multi-metric solution for use in the assessment of individuals with confirmed or suspected fatty liver disease. From one quick, non-invasive MRI scan, doctors have access to a suite of metrics relating to a patient’s liver health.
HepaFat-AI produces these patient results for clinician interpretation within seconds, providing accurate, reliable and reproducible results across MRI centres and scanner models.
HepaFat-AI is ideally suited for single and multi-center clinical trials in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD).
HepaFat-AI has received 510(k) clearance from the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA), European CE marking, and approval from the Australian Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA).
HepaFat-AI can be deployed either in the cloud or on premises and can be integrated directly into radiology workflows. For current availability, please contact us directly.
Comprehensive all-in-one Reporting
HepaFat-AI performs fully automated and comprehensive all-in-one liver fat analysis and reporting:
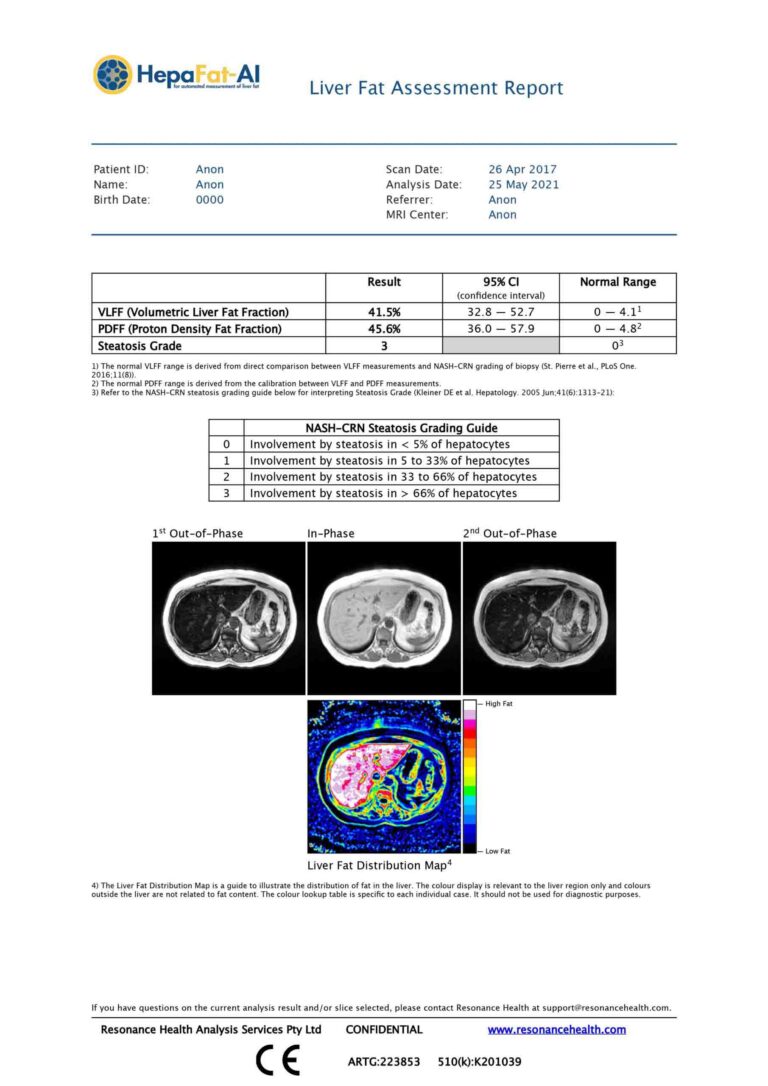
- VLFF – (Volumetric Liver Fat Fraction)
- PDFF – (Proton Density Fat Fraction)
- Steatosis Grade
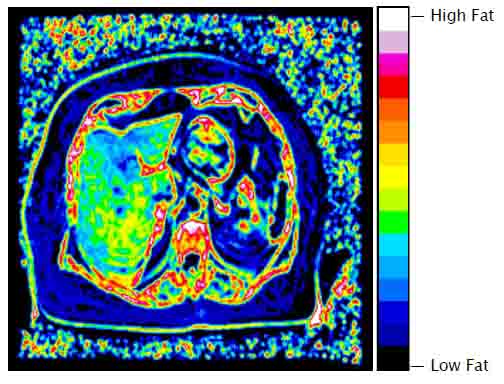
- Liver Fat Distribution Map
In the event that extremely high liver fat content is detected, the HepaFat AI analysis process will generate a different report with a warning message that indicates the value is outside the validated calibration range and that the associated uncertainty makes a precise estimate too unreliable for reporting.
In the event that high liver iron concentration is suspected, or that there is possible lung crest present due to incorrect slice position, a warning is given and no result will be shown on the generated HepaFat-AI report.
Steatosis Grading
- Provides a validated NASH-CRN histopathological steatosis grading;
- The only regulatory cleared MRI method capable of reporting a steatosis grading.
Proton Density Fat Fraction (PDFF)
- PDFF has been widely shown to correlate with the degree of hepatic steatosis, with a cut-off of 5% being indicative of NALFD;
- The only regulatory cleared MRI method capable of reporting a steatosis grading.
Volumetric Liver Fat Fraction (VLFF)
- Provides an MR liver fat metric that correlates with hepatocyte macrovesicular fat volume;
- Enhanced signal to noise acquisition for improved performance.
Key HepaFat-AI Features
- An accurate and validated MRI-based measurement of liver fat
- Non-invasive and contrast free with a rapid scan time of only two minutes in a single breath hold
- Quantitative results available in real-time
- Notifies in cases of suspected high liver iron content
- Fits easily into existing workflows
- International regulatory clearance (USA - FDA, Europe - CE Marking, Australia - TGA)
- Comprehensive all-in-one reporting (VLFF, PDFF, and Steatosis Grade)
- Accurate, reliable and reproducible across MRI centres and scanner models
- Fully standardised work flow processing from image acquisition to analysis and report generation
- Ideally suited for single and multi-center NASH clinical trials
- No new MRI scanner hardware or software required
- Suitable for 1.5 and 3 Tesla MRI scanners
Why Use HepaFat-AI to Measure Liver Fat
HepaFat-AI is quick, easy and painless, with an MRI scan time of only two minutes. HepaFat-AI does not require any contrast agents and being MRI based there is no risk from ionising radiation. Due to the automated nature of the technology, HepaFat-AI can also return a patient report in real-time back to the clinician.
Histopathological assessment of a patient’s liver fat levels from a liver biopsy is commonly considered the gold standard for clinical assessment of liver fat. However, it is subjective, has a poor reproducibility and significant sampling error and suffers from the risks associated with an invasive procedure.
Ultrasound, while widely available, only has a sensitivity of approximately 70% and this is further reduced in obese patients. It is additionally hampered by factors such as fibrosis, edema and extrahepatic adipose tissue.
CT is also a widely available imaging modality that evaluates hepatic steatosis indirectly based on hepatic x-ray attenuation. Several factors other than fat (e.g. iron, copper, glycogen, fibrosis, edema, ingestion of drugs such as amiodarone and gold) affect CT attenuation values, resulting in unavoidable errors in fat quantification and low sensitivity for mild-moderate steatosis. Moreover, as CT relies on ionizing radiation, it is not suitable for use in children and for longitudinal monitoring of adults with liver fat. MR has also been used for quantitative assessment of fat and is widely accepted as superior compared to ultrasound and CT.
HepaFat-AI is used in conjunction with a specific MRI data acquisition protocol that is a variation of the Dixon Method. Many MR fat quantification methods such as Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy (MRS) and other Dixon based imaging methods report the fat:water proton ratio. This ratio is not directly comparable to a fat measurement from a liver biopsy specimen as it neither represents the percentage of parenchyma involved with fat nor the volume fraction of fat in the biopsy. Resonance Health has addressed this issue with HepaFat-AI.
Potential Clinical Applications
Gastroenterology and Hepatology Applications
- Initial workup for Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) diagnosis and for education and counselling of metabolic syndrome patients.
- Liver fat analysis on patients already being screened or monitored for fibrosis or cirrhosis. Recent research indicates that patients with NAFLD and Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH) can develop liver cancer without progressing through cirrhosis and that higher liver fat in NAFLD is associated with fibrosis progression.
- Screening and monitoring of participants for early-phase pharmaceutical trials of compounds to treat NASH or diabetes.
Surgical Applications
- Pre and post-operative analysis of bariatric patients to track clinical outcomes. Bariatric patients post-surgery can see a dramatic improvement in liver fat regardless of their starting anthropometrics (e.g. weight, BMI,) or amount of weight loss following surgery.
- A high level of liver fat may have a detrimental outcome on liver surgery. A HepaFat-Scan of patients with liver disease or liver cancer can provide guidance with treatment planning. A quantitative measurement of liver fat may help to determine how much liver can be safely resected or to determine whether to use a surgical or non-surgical treatment.
- Screening for suitability of living donors for liver transplants by assisting in determining the viability of the donor liver.
Applications by Primary Care Physicians
- HepaFat-Scan may be useful to screen patients prior to prescribing known hepatotoxic medications.
- Monitoring of patients undergoing an intervention (e.g. limiting alcohol consumption or weight loss).
- Monitoring of patients prescribed medications known to induce steatosis.
How does HepaFat-AI work?
HepaFat AI is based on the Dixon principle of measuring the in-phase and out-of-phase MRI signal in liver tissue. Measurements are achieved through the acquisition of a series of spoiled gradient recalled echo images at three specific echo times.
The process from data upload to report generation takes under 60 seconds for completion. HepaFat AI has been extensively validated to ensure the results are accurate and reproducible.
HepaFat-AI via Resonance Health
HepaFat-AI is a stand-alone software application that automatically analyses MRI (DICOM) images that are uploaded via the Resonance Health web portal. These images, acquirable on most makes and models of 1.5 and 3 Tesla MRI machines, are obtained through a unique and standardised scanning sequence to ensure results are accurate, reliable, and reproducible over time and between hospitals and the various makes and models of MRI scanners.
The entire HepaFat-AI analysis process is completely automated. The HepaFat-AI technology will initially inspect all images to ensure that they have been acquired with the correct protocol. If errors are detected in the method of data acquisition, HepaFat-AI will not analyse the data but will indicate the corrective steps that need to be taken to acquire compliant images. Uploading and analysis of data typically takes about 30 seconds.
Due to the quality-controlled, standardised nature of the test, a patient may have HepaFat-AI analysis at any HepaFat-verified MRI centre, anywhere in the world.
HepaFat-AI Resources
Click the link(s) below to access our resources. Need something else? Please contact our team at [email protected] for further information.